Introduction
Homeowners insurance is one of the most important investments you can make as a homeowner. It protects your home and belongings from unexpected events such as fires, theft, and natural disasters. However, with so many options available, it can be overwhelming to choose the right policy for your needs. In this guide, we will walk you through the factors to consider when comparing homeowners insurance policies, helping you make an informed decision and find the best coverage for your home.
1. What is Homeowners Insurance?
Homeowners insurance is a type of property insurance that covers a private residence. It provides financial protection in the event of damage to your home or belongings due to covered events, such as fire, vandalism, burglary, or certain natural disasters. In addition to covering damage to your property, homeowners insurance typically includes liability coverage, which protects you in case someone is injured on your property.
While homeowners insurance is not legally required, most mortgage lenders will require you to have it in place to protect the value of the home and the lender’s investment.
2. Why is Homeowners Insurance Important?
Homeowners insurance is important for several reasons:
a. Protection of Property
One of the most obvious reasons for having homeowners insurance is to protect your home and belongings. If your house is damaged by fire, hail, or other covered events, homeowners insurance helps cover the cost of repairs or rebuilding, as well as replacing damaged or stolen personal property.
b. Liability Protection
Homeowners insurance provides liability coverage if someone is injured on your property. This can include medical expenses, legal fees, and any potential settlements related to an injury or accident on your premises.
c. Financial Security
Without homeowners insurance, the cost of repairing or replacing your home and belongings after a disaster could be financially devastating. Insurance provides financial security by covering these expenses and reducing the impact of unexpected events.
d. Mortgage Requirement
Most mortgage lenders require homeowners insurance as part of the loan agreement. This ensures that the lender’s investment is protected in the event of property damage or destruction.
3. Types of Homeowners Insurance Policies
When comparing homeowners insurance policies, it’s important to understand the different types of coverage available. Here are the most common types:
a. HO-1: Basic Coverage
HO-1 is the most basic homeowners insurance policy. It provides limited coverage for specific perils, such as fire, lightning, and theft. While it offers the lowest premiums, it provides minimal protection and is rarely offered by insurers today.
b. HO-2: Broad Coverage
HO-2 is a broad form policy that provides coverage for a wider range of perils than the basic HO-1 policy. It typically covers damage from fire, theft, vandalism, windstorms, hail, and more. However, it is still limited in scope and may not cover some of the more complex risks.
c. HO-3: Special Coverage
HO-3 is the most common type of homeowners insurance policy. It provides coverage for the structure of your home against all perils, except for those explicitly excluded in the policy (such as floods or earthquakes). Personal property is typically covered on a named-perils basis, which means only specific risks are covered, such as fire or theft.
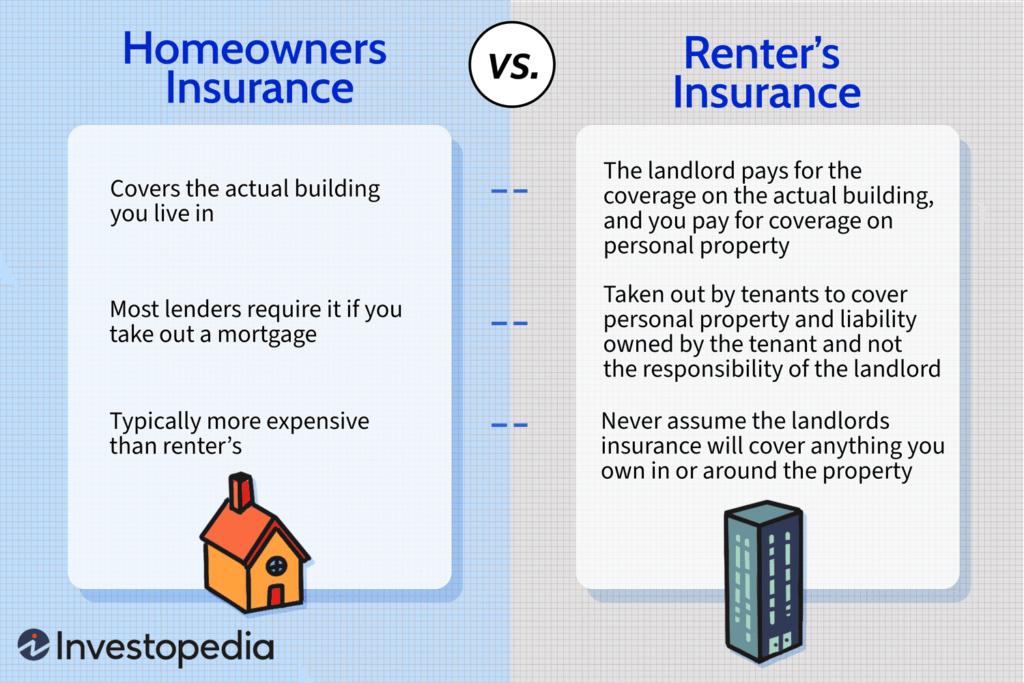
d. HO-4: Renters Insurance
HO-4 is designed for renters, not homeowners. It provides coverage for personal belongings in a rented space and liability protection. However, it does not cover the structure of the building itself, which is the responsibility of the landlord.
e. HO-5: Comprehensive Coverage
HO-5 offers the most extensive protection for both the structure of your home and personal belongings. It covers all risks, except for those specifically excluded. Additionally, personal property is covered on an open-perils basis, meaning it is covered for any risk that is not excluded in the policy.
f. HO-6: Condo Insurance
HO-6 is designed for owners of condominiums or co-ops. It provides coverage for personal property, liability, and the interior structure of the unit, but it does not cover the building itself, which is typically covered by the condo association’s master policy.
g. HO-7: Mobile Home Insurance
HO-7 provides coverage for mobile or manufactured homes. It covers similar risks to standard homeowners insurance policies but is specifically tailored to the unique risks associated with mobile homes.
h. HO-8: Older Home Insurance
HO-8 is designed for older homes that may not meet modern building codes. It provides coverage based on the actual cash value (ACV) rather than the replacement cost, which can be useful for homes that have a lower market value but are expensive to repair or replace.
4. Key Factors to Consider When Comparing Homeowners Insurance
When comparing homeowners insurance policies, there are several factors to consider to ensure you get the best coverage at an affordable price. Here are the key elements to keep in mind:
a. Coverage Limits
Each homeowners insurance policy has coverage limits, which represent the maximum amount your insurer will pay for a claim. These limits should be sufficient to cover the full replacement cost of your home and belongings. Ensure that the policy limits align with the value of your property and possessions.
b. Deductibles
The deductible is the amount you must pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Generally, higher deductibles result in lower premiums, but they also mean that you will have to pay more in the event of a claim. Consider how much you can afford to pay out-of-pocket when choosing your deductible.
c. Exclusions
It’s important to understand the exclusions in your policy. Common exclusions include damage from floods, earthquakes, and routine wear and tear. If you live in an area prone to certain risks (e.g., flooding), you may need to purchase additional coverage for these perils.
d. Replacement Cost vs. Actual Cash Value
When reviewing policies, you’ll encounter two types of coverage for personal property: replacement cost and actual cash value (ACV). Replacement cost covers the cost of replacing items without factoring in depreciation, while ACV takes depreciation into account. Replacement cost coverage is typically more expensive but offers better protection.
e. Additional Coverage Options
Many insurers offer additional coverage options, such as flood insurance, earthquake insurance, and personal property endorsements for high-value items (e.g., jewelry, art). If you have specific needs, such as coverage for a home office or valuable collectibles, be sure to ask about these add-ons.
5. How to Compare Homeowners Insurance Quotes
To find the best homeowners insurance policy for your needs, it’s essential to compare quotes from multiple providers. Here are some tips for doing so:
a. Gather Information
Before requesting quotes, gather information about your home, including its age, square footage, location, and any security features. You’ll also need to know the value of your personal property and any additional coverage you may require.
b. Use Online Comparison Tools
Many websites offer tools to compare homeowners insurance quotes from multiple insurers. These tools allow you to input your information and receive quotes quickly, making it easier to find the best deal.
c. Review Policy Details
When comparing quotes, don’t just focus on the premium. Review the policy details, including coverage limits, exclusions, and any additional coverage options. Ensure that each quote provides the same level of coverage so you can make an apples-to-apples comparison.
d. Check the Insurer’s Reputation
The reputation of the insurance company is also an important factor to consider. Look for an insurer with a strong financial rating, positive customer reviews, and a good track record of handling claims efficiently.
6. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What does homeowners insurance cover? Homeowners insurance typically covers damage to your home, personal property, and liability for accidents that occur on your property. Coverage may also include additional living expenses if you’re temporarily displaced due to damage.
Q2: Is homeowners insurance required by law? Homeowners insurance is not required by law, but most mortgage lenders require it to protect their investment in the home.
Q3: What is the difference between replacement cost and actual cash value? Replacement cost covers the full cost of replacing your damaged property, while actual cash value accounts for depreciation, paying you less than the cost of replacement.
Q4: Does homeowners insurance cover natural disasters? Homeowners insurance generally covers damage from certain natural disasters, such as windstorms and hail, but may exclude coverage for floods, earthquakes, or other events. You may need to purchase separate coverage for these risks.
Q5: Can I add additional coverage to my homeowners insurance policy? Yes, many insurers offer additional coverage options, such as flood insurance, earthquake insurance, or coverage for valuable items like jewelry. You can add these to your policy based on your needs.
7. Conclusion
Comparing homeowners insurance policies is essential for finding the best coverage at an affordable price. By understanding the different types of policies, evaluating your home’s needs, and carefully reviewing quotes from multiple insurers, you can ensure that your property and belongings are adequately protected. With the right homeowners insurance, you’ll have peace of mind knowing that you’re prepared for unexpected events, allowing you to focus on enjoying your home and safeguarding your future.
